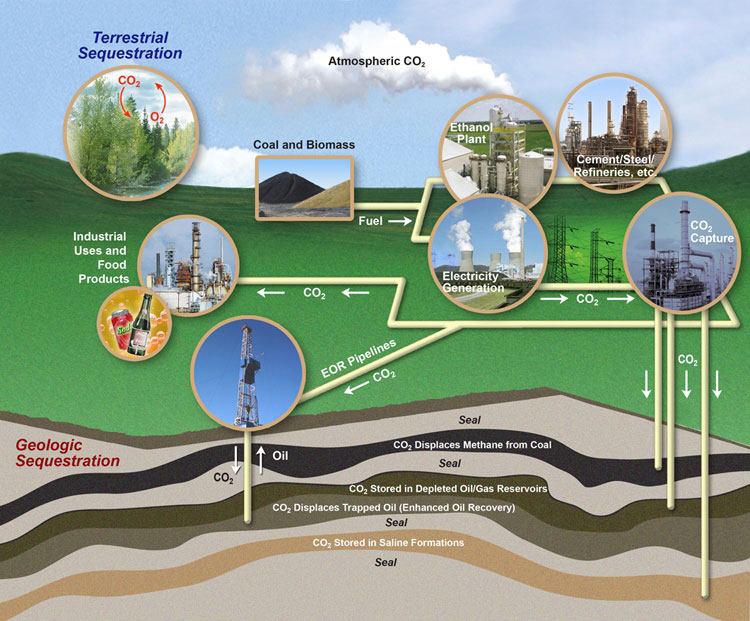
Carbon sequestration is the capture of carbon dioxide (CO2) and may refer specifically to:
"The process of removing carbon from the atmosphere and depositing it in a reservoir.
It is also referred to as carbon dioxide removal, which is a form of geoengineering.
The process of carbon capture and storage, where carbon dioxide is removed from flue gases, such as on power stations, before being stored in underground reservoirs.
Natural biogeochemical cycling of carbon between the atmosphere and reservoirs, such as by chemical weathering of rocks.
Carbon sequestration describes long-term storage of carbon dioxide or other forms of carbon to either mitigate or defer global warming. It has been proposed as a way to slow the atmospheric and marine accumulation of greenhouse gases, which are released by burning fossil fuels.
Carbon dioxide is naturally captured from the atmosphere through biological, chemical or physical processes. Some anthropogenic sequestration techniques exploit these natural processes,
Artificial processes.
Carbon dioxide may be captured as a pure by-product in processes related to petroleum refining or from flue gases from power generation.
CO2 sequestration includes the storage part of carbon capture and storage, which refers to large-scale, permanent artificial capture and sequestration of industrially produced CO2 using subsurface saline aquifers, reservoirs, ocean water, aging oil fields, or other carbon sinks.

Hindu dated 5.10.11
ReplyDeleteIceland's carbfix experiment seeks to separate CO2 from steam on volcanic field and pump it underground to react with porous basalt rock,forming limestone,in order to lock CO2 in harmless form.
Hindu dated 5.10.11
ReplyDeleteIceland's carbfix experiment seeks to separate CO2 from steam on a volcanic field and pump it underground to react with porous basalt rock,forming limestone,in order to lock CO2 in harmless form.